Video: Flat Feet in Children – What Parents Need to Know
Does your child have feet that are flatter than normal? Although sometimes this is nothing to worry about, in other situations flat feet can lead to pain and long-term damage to the feet. We specialize in the foot problems of children and can help you determine if your child’s flat feet are something to worry about. Make an appointment for your child in our Seattle clinic if you are concerned.
What is Child Flat Foot?
“Flatfoot” (also known as pes planus) is a condition where the foot lacks an arch on the inside. While the exact incidence of this condition in children is unknown [1], we do know that it is very common. Given that almost all children start out with little or no arch, do flat feet pose a real problem? When, if ever, is it appropriate to intervene? Are arch supports, special shoes, or in-shoe orthotics necessary?
Almost every child’s foot initially has a large fat pad on the inside arch which slowly decreases as they grow. Most kids eventually develop a normal arch
It is important, however, to differentiate a normal, flexible flatfoot from other more serious flatfoot deformities. These more serious problems are often due to a bony deformity, such as an abnormal fusion of one or more bones. Determining the existence of a rigid flatfoot can be easily done in our Seattle office.
Is Treatment of Flat Feet in Children Necessary?
When a child presents with flat feet, our first goal is to determine if your child is currently having, or is likely to have, any problems related to their flat feet. Remember, sometimes flat feet can cause serious problems, but sometimes a person is meant to have flatter feet and that’s just normal for them. Many kids with flat feet do not need any treatment (and by treatment we are usually referring to the use of either prefabricated or custom orthotics to support the feet). Some kids with flat feet, however, will benefit from treatment to either treat current problems or prevent future problems.
Immediate problems from flat feet can include:
- Pain of the feet, ankles, knees or back
- Lack of coordination
- Desire not to participate in sports
- A desire to be carried more than other kids their age
- Structural changes in the bones and joints such as formation of bunions or bone spurs
Long term problems related to flat feet can include:
- Development of deformities such as bunions, hammertoes or bone spurs
- Development of arthritis
- Unstable ankles and frequent sprains
- Pain the feet, ankles, knees, hips and back
By evaluating your child’s feet and gait we can usually determine what kind of problems, if any, your child is likely to suffer as a consequence of their flat feet.
The Importance of Family History in Flat Feet Treatment
Another reason to consider treatment of flatfoot is family history. If Dad or Mom, for example, have flat feet and have had a history of foot problems that are likely related to the flat feet then we are more likely to use prefabricated or custom orthotics to protect your child’s feet.
If your child is (or is likely to) suffering any problems caused by their flat feet, then treatment will be started. Treatment is aimed at relieving pain, improving gait and preventing future problems. Usually this is through the use of either prefabricated or custom orthotics. Shoe and exercise recommendations are also common.
How are Flat Feet in Kids Treated?
Treatment usually includes the use of either prefabricated or custom orthotics designed to do the following:
- Support the foot with proper shoes and prefabricated or custom orthotics
- Eliminate pain
- Encourage normal development of the arch,
- Prevent pelvic and spinal postural deformities 1.
We will also provide you with information about proper shoes for your child and discuss exercises that can prevent problems.
There is some evidence that early use of orthotics can help encourage normal arch development. If your child is 8 or older, the flexible flatfoot can be considered permanent, and long-term use of orthotics will often be required to prevent future problems in the feet, lower extremities, and spine. This is especially true for overweight or athletically active youngsters.
Research on the use of orthotics to treat flat feet is ongoing. An interesting 2014 study showed that after 24 months of using custom orthotics, children with flat feet had more normal looking feet on x-ray. This may indicate that use of orthotics in kids with flat feet can prevent flat foot related problems like bunions and arthritis.2
Should Kids with Flat Feet Use Prefabricated Orthotics or Custom Orthotics?
Our general recommendation is to use the least expensive treatment that gives the best protection. There are some very good over-the-counter arch supports available that are made specifically for kids with flat feet and we use these a majority of the time. They are quite inexpensive and can be easily changed as the child grows.
If you want to try a good over-the-counter support we often recommend the PowerStep PowerKids arch support. These are an excellent  OTC arch support for kids with flat fee and are available in sizes that will fit early walkers up through big kids.
OTC arch support for kids with flat fee and are available in sizes that will fit early walkers up through big kids.
While these are a very good arch support on their own, we often modify them for our patients to improve their support.
For children who are wearing adult shoe sizes we recommend the FootChair Medical Grade Adjustable Orthotic since the arch can be adjusted for maximum support and comfort via pads that can be inserted under the cover.
Custom orthotics are a great value for adults who will wear them for many years, but can be expensive when kids are at a stage when they might grow out of them every year or two. Thus, we will reserve the use of custom orthotics for children with only the very worst flat feet or those who do not respond to the prefabricated orthotics.
Whether a prefabricated or a custom orthotic is used, there are some specific orthotic features that must be present in order to best support a flat foot. This includes a deeper than average cup around the heel, wedging in the heel cup of the orthotic to support the heel and a “medial flange” to support the arch. 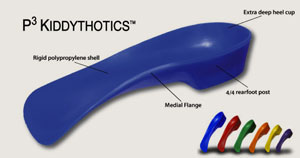
In our clinic we use a somewhat more supportive prefabricated orthotic than the PowerStep. The P3 Kiddythotic is designed specifically for kids with flat feet. It is currently available only in medical clinics.
What if One Foot is Flatter than the Other?
Having one foot latter than the other is a more serious problem as these asymmetrical forces imposed during activities can eventually result in significant cumulative trauma to the foot/ankle complex, knees, hips, and low back 1. If one foot is flatter than the other, the child is more likely to require custom orthotic therapy.
Home Treatment of Child Flatfoot
- Strengthen the child’s lower leg muscles with home exercises, especially Tibialis Posterior, and Internal/External Rotation exercises. Also, have the child perform the towel-gathering exercise (‘scrunching’ a towel lying on the floor with the toes) for 15 minutes daily.
- Insist the child wear supportive shoes with a stable heel (not worn down on either side) and a strong counter (the shoe material that fits around the heel of the foot).
- You can try some prefabricated arch supports. You can see our recommended arch supports for children here.
- If excessive pronation and flatfoot are noted to persist as the child matures, correction with custom-made orthotics is indicated.
Shoes for Kids with Flat Feet
Proper shoes are important for the developing foot; but, the proper type of shoe is dependent on what type of foot your child has. Details on shoes for children is available here. Kids with flat feet often require a more stable shoe. Be sure to bring a selection of your child’s shoes in when you bring them in to see us for an evaluation.
Medical References for Child Flat Feet
- Sullivan JA. “Pediatric flatfoot: evaluation and management.” J Am Acad Orthop Surg 1999; 7(1):44-53.
- Notari MA. “A study of the incidence of pedal pathology in children.” J Am Pod Med Assn 1988; 78:518-521.
- Wetton EA. “The Harris and Beath footprint: interpretation and clinical value.” Foot & Ankle 1992; 13:462-468.
- 1Hoppenfield S. “Physical Examination of the Spine and Extremities.” New York: Appleton-Century-Crofts, 1976:232.
- Luhmann SJ, Rich MM, Schoenecker PL. “Painful idiopathic rigid flatfoot in children and adolescents.” Foot Ankle Int 2000. 21(1):59-66.
- Kuhn DR, Shibley NJ, Austin WM, Yochum TR. “Radiographic evaluation of weight-bearing orthotics and their effect on flexible pes planus.” J Manip Physiol Ther 1999; 22(4): 221-226.
- 2Soo-Kyung Bok, MD, et. al. “Effects of Custom-Made Rigid Foot Orthosis on Pes Planus in Children Over 6 Years Old”. Ann Rehabil Med. 2014 Jun;38(3):369-375





